TImageEnProc.Crop
Declaration
// Standard overloadprocedure Crop(x1, y1, x2, y2 : Integer; FillColor: TColor = -1); overload;
// TRect overloads
procedure Crop(Rect : TRect; FillColor: TColor = -1); overload;
// TRect with rotation overload
procedure Crop(Rect: TRect; Rotation: double; AntialiasMode: TIEAntialiasMode = ierFast); overload;
// Shape cropping overload
procedure TImageEnProc.Crop(x1, y1, x2, y2: Integer; Shape: TIEShape; FillColor: TColor = clNone; AdjustAspectRatio: Boolean = False; Angle: Integer = 0; ShapeModifier: Integer = 0; AntiAlias: Boolean = True);
// Perspective fix overload
procedure Crop(Quadrilater: array of TDPoint); overload;
Description
Replace the current image with the content of the specified rectangle (i.e. remove everything outside the specified region).You can also use negative or out-of-range values to enlarge the image. If this case, FillColor will be used for the new areas. If -1 is specified, the default background is used. If clNone, then the non-image area will become transparent.
Some overloads also allow rotation (which will occur before the crop occurs. See below). Angles are specified as degrees clockwise.
The Shape overload allows you to crop the image into one of many available shapes. If FillColor is clNone, the removed area will become transparent, otherwise the alpha is merged with the specified color.
The Perspective fix overload allows you to adjust images that have perspective distortion. You need to specify the four points that will become the corners of the new image. The order is as follows:
◼Top-Left corner
◼Top-right corner
◼Bottom-right corner
◼Bottom-Left corner

Note:
◼Values are in terms of the bitmap (not the screen)
◼Specified values are inclusive, so the resulting width will be x2-x1+1. The height will be y2-y1+1.
◼Use CropSel to crop to the current selection
◼A UI for this is available to your users in the Image Processing dialog
◼To crop a selection, use CropSel
Rotate and Crop Explanation
The Rotate and Crop overload rotates the whole image and the crops to a region of interest by adjusting the crop region to account for the rotation.Consider this image:

And these parameters:
const
Rotation_Angle = 10;
Crop_Left = 220;
Crop_Top = 70;
Crop_Right = 220 + 170;
Crop_Bottom = 70 + 160;
Cropping then rotating:
ImageEnView1.IO.LoadFromFile( 'D:\Tiger.jpg' );
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( Crop_Left, Crop_Top, Crop_Right, Crop_Bottom );
ImageEnView1.Proc.Rotate( Rotation_Angle, ierBicubic, clBlack );

Rotating then cropping:
ImageEnView1.IO.LoadFromFile( 'D:\Tiger.jpg' );
// Note the negative rotation value
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( Rect( Crop_Left, Crop_Top, Crop_Right, Crop_Bottom ), -Rotation_Angle, ierBicubic );

Demo
 | Demos\ImageEditing\EveryMethod\EveryMethod.dpr |
Examples
// Crop the image at the bitmap position, Top-Left: (150, 100), Bottom-right: (450, 300). The specified range is maintained, so the resulting image will be 301 x 201 pixelsImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( 150, 100, 450, 300 );
// Which is the same as...
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( rect( 150, 100, 450, 300 ) );
// And also the same as...
ImageEnView1.SelectionBase := iesbBitmap;
ImageEnView1.Select( 150, 100, 450, 300 );
ImageEnView1.Proc.CropSel();
// Crop to the selected area of the image (same as ImageEnView1.Proc.CropSel)
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( ImageEnView1.SelectedRect.x,
ImageEnView1.SelectedRect.y,
ImageEnView1.SelectedRect.x + ImageEnView1.SelectedRect.Width,
ImageEnView1.SelectedRect.y + ImageEnView1.SelectedRect.Height );
// Crop to the bitmap rect 100,100,300,200 and rotate image 20 deg. clock-wise
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( rect( 100, 100, 300, 200 ), 20, ierBicubic );
// Crop to the specified quadrilateral (4 points that will become the new corners) and apply forward perspective mapping. Useful to adjust perspective distortion
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop([ DPoint(104, 85), // Top-Left corner
DPoint(1000, 150), // Top-right corner
DPoint(181, 500), // Bottom-right corner
DPoint(54, 400) // Bottom-Left corner
]);
// Fix a parallelogram
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop([ DPoint(50, 0), DPoint(500, 0), DPoint(450, 400), DPoint(0, 400)]);
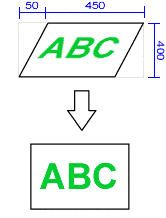
// Crop 25% of all sides of the image
ImageEnView1.IO.LoadFromFile( 'D:\TestImage.jpg' );

ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width div 4,
ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height div 4,
MulDiv( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width, 3, 4 ),
MulDiv( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height, 3, 4 ));

// Crop 10% from top-left corner, and 30% from bottom-right corner and stretch
// by specifying 4 points (which will become the new corners)
x1 := MulDiv( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width, 10, 100 );
y1 := MulDiv( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height, 10, 100 );
x2 := ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width - MulDiv( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width, 30, 100 );
y2 := ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height - MulDiv( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height, 30, 100 );
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop([ DPoint( x1, y1 ), // Top-Left corner
DPoint( ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width, 0 ), // Top-right corner
DPoint( x2, y2 ), // Bottom-right corner
DPoint( 0, ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height ) // Bottom-Left corner
]);

// Crop in a perfectly circular shape
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( x, y, x + sz, y + sz, iesEllipse, clNone, True );

// Crop the image to a random shape
ImageEnView1.Proc.Crop( 0, 0, ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Width, ImageEnView1.IEBitmap.Height, TIEShape( Random( ord( High( TIEShape )) - 1 )), clNone, False );



See Also
◼CropSel◼Global Image Methods